
Broadcasting Arrays - A Highly Parallel Computer Architecture Suitable For Easy Fabrication. |-o A8 is attacked by white rook from south A common example of a circuit employing sequential logic is the flip-flop, also called a bistable gate. This is the electronics questions and answers section on Sequential Logic Circuits with explanation for various interview, competitive examination and. Each of the inputs and output (s) can attain either of two states: logic 0 (low) or logic 1 (high).
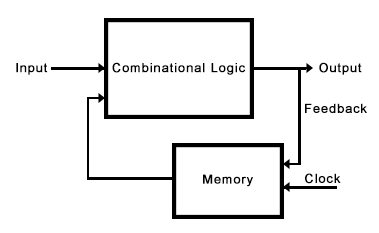
Behavior of an asynchronous sequential circuit depends. Sequential logic is a form of binary circuit design that employs one or more inputs and one or more outputs, whose states are related by defined rules that depend, in part, on previous states. O-/64/- empty(square) -/64/-| 64:1 |->| |-o result reliable / otherwise processing after reset The major difference between combinational and sequential logic circuit is that the combinational logic circuit consists of only logic gates while the. This type of logical circuit is also known as clocked sequential circuits. state changes in sequential circuits only occur when the clock ticks.
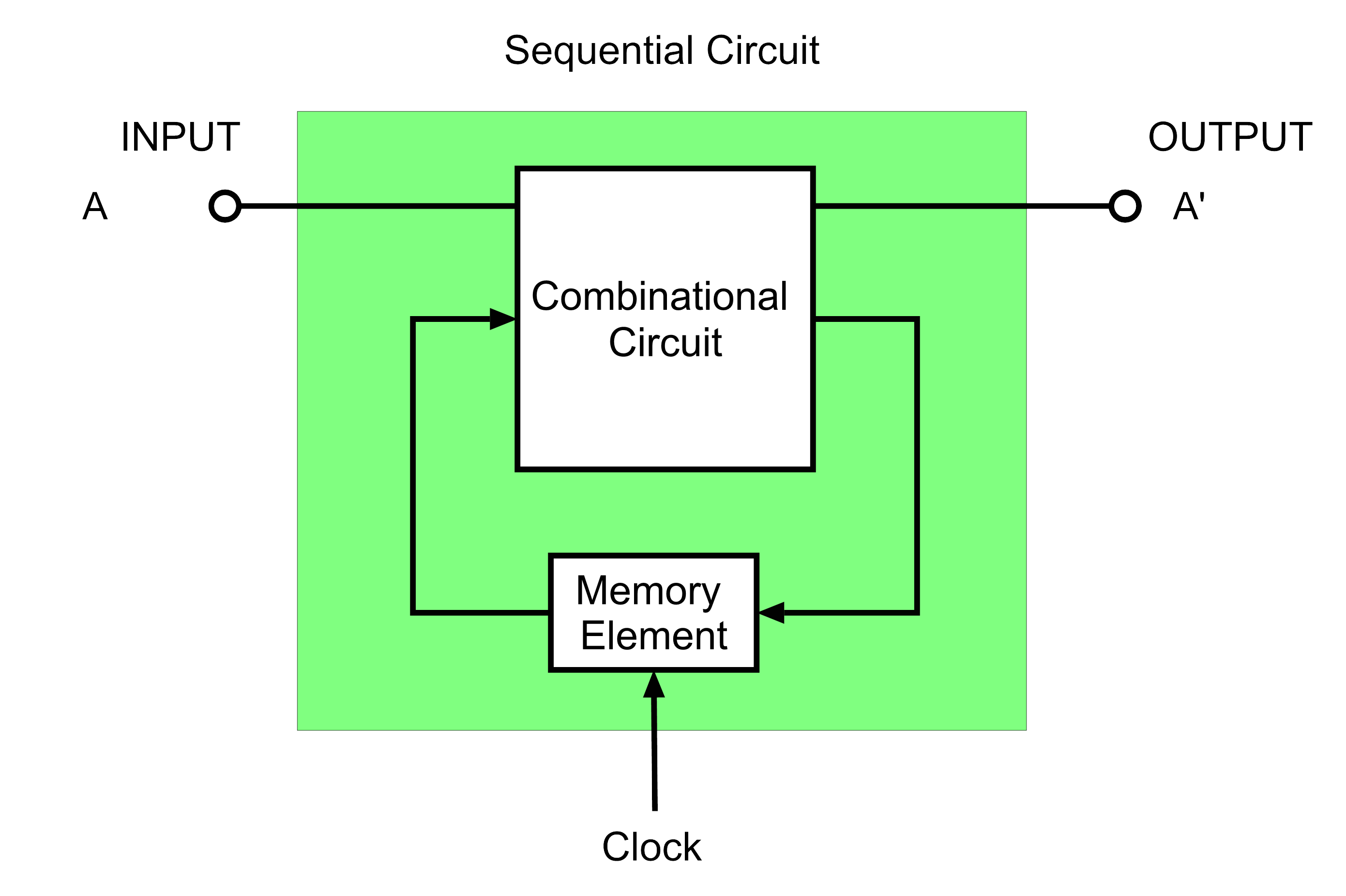
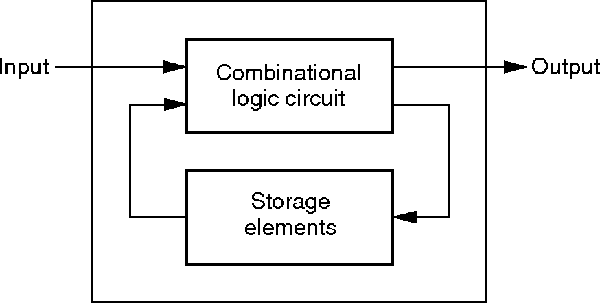
Sequential logic, that is combinatorial logic combined with memory, is the base of Finite-state machines, Turing machines as well as digital computers.Īs an further example, a sequential logic may perform the same task as mentioned in Combinatorial Attack and Defend Map, but with less gates in up to seven cycles - similar to the bitboard techniques like Dumb7Fill: The word Sequential means that things happen in a sequence, one after another and in Sequential Logic circuits, the actual clock signal determines when. whereas sequential logic output depends on stored levels and also the input levels.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
